Language Updates
Breaking Changes
-
Error Handling Syntax: The syntax for error handling has changed from
f(x)!tof!(x). This change facilitates IDE auto-completion, allowing the function name and!to be completed together and enabling special rendering forf!. -
Local Functions: If a local function can return an error type, it must be annotated. For example:
fn toplevel() -> Unit!String {
fn local1() -> Unit!String { raise "err" } // local function
fn local2() -> _!_ { raise "err" } // local function
apply!(fn (_x) -> Int!String { raise "err" }, 42) |> ignore // anonymous function
}
fn apply(f: (Int) -> Int!String, x: Int) -> Int!String {
f!(x)
}
Additionally, the fn! and fn local!() syntax can be used to indicate that a function might return an error and to let the compiler infer the error type. The former is used for lambda and anonymous functions, and the latter for regular local functions. For example:
fn toplevel() -> Unit!String {
fn local!() { raise "err" } // local function
apply!(fn! (_x) { raise "err" }, 42) |> ignore // anonymous function
apply!(fn! { _ => raise "err" }, 42) |> ignore // lambda function
}
Try Expression Enhancements
The try expression has been improved. The complete usage of the try expression is as follows:
fn test_try() -> Unit {
fn f() -> Int!String {
raise "err"
}
try {
println("this is try body")
f!()
} except {
err => println(err)
} else {
val => println(val)
}
}
- The
exceptkeyword is used to handle errors returned by the try body. - The
elsekeyword is used to handle normal returns from the try body.
Simplified cases for the try expression:
- The
elsebranch can be omitted if no handling of the return value is needed. - The
trybody can be a simple expression. - The
exceptkeyword can be omitted.
For example:
fn test_try() -> Result[Int, String] {
fn f() -> Int!String {
raise "err"
}
try Ok(f!()) { err => Err(err) }
}
Integer Literal Overloading in Pattern Matching
Integer literal overloading has been added to pattern matching:
fn is_42(x : Double) -> Bool {
match x {
42 => true
_ => false
}
}
Upcoming Breaking Changes
-
Map Pattern Matching: The semantics of
{ "key" : value }in map patterns will be changed this week.Previously, in a map pattern,
valuewas of typeOption[_]and would match regardless of whether"key"existed.In the future,
{ "key": value }will match only if"key"exists, andvaluewill directly match the actual content of"key".To match both the presence and absence of
"key", use the new syntax{ "key"? : value_or_none }, wherevalue_or_noneis of typeOption[_]. -
Trait Implementation Syntax: The old syntax for explicit trait implementation
fn Trait::method(...)will be removed this week. Existing code should use theimpl Trait for SelfType with method(...)syntax. Thefn Trait::method(...)syntax will be repurposed for defining methods on trait object types in the future.
IDE Updates
- Run | Debug Codelens for the main function: The main function will now have a Run | Debug Codelens for quick execution and debugging. Currently, quick debugging only supports the JavaScript backend.
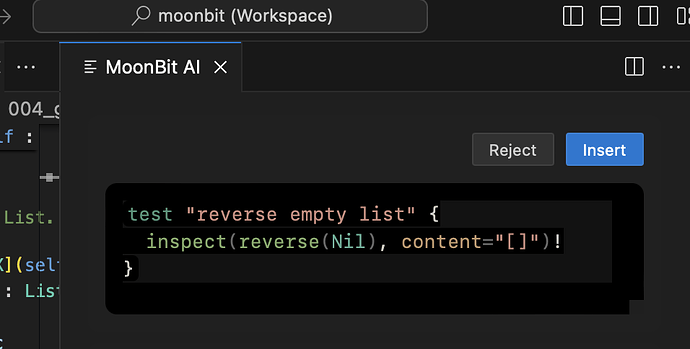
-
AI-Generated Tests for Top-Level Functions: Top-level functions now support generating tests through AI via Codelens. * Please note that this feature is still under development and may not be stable.
- Click the “Gen test” button.

- A new window will appear on the right side, displaying the generated test.
- Click “Reject” to remove unwanted tests, or “Insert” to add the test into the source file.
Core Updates
ShowTrait Redefinition: TheShowtrait has been redefined for more accurate behavior. The new definition of theShowtrait is as follows:
pub trait Show {
// The `output` function is for implementing `Show` for composite types.
// It writes a string representation of `Self` to a `Logger`.
output(Self, Logger) -> Unit
// The `to_string` method is for `Show` users.
// It can be used for string interpolation and `println`.
// `to_string` has a default implementation using `output`.
// Some types, like `String`, will override `to_string` to modify its behavior.
to_string(Self) -> String
}
The new Show resolves the incorrect behavior of String. Previously, if a composite type contained a String, the Show implementation would not escape this String, leading to incorrect results. Conversely, String used directly in string interpolation and println should not be escaped. The new Show definition and its core implementation address both needs.
For Show implementers, please keep in mind:
-
Implement the
outputmethod, not theto_stringmethod. -
When recursively calling the
Showimplementation of substructures (e.g., struct fields), useShow::output(..., logger)instead ofto_string. -
The default implementation of
Show::to_stringis not a method, so it cannot be called with a dot. To support.to_string()syntax, add a helper definition like this:
pub fn to_string(self: ...) -> String {
Show::to_string(self)
}
-
Upcoming Breaking Change: Deprecation of
DebugTrait: Following the redefinition of theShowtrait, the functionality of theDebugtrait is now completely covered byShow. Therefore, theDebugtrait is deprecated and will be removed soon. -
Data Structure Type Renaming: Data structure type names have been changed to
T. For example:
// old
// let m : @hashmap.HashMap[Int, Int] = @hashmap.new()
// new
let m : @hashmap.T[Int, Int] = @hashmap.new()
The following data structures have been renamed to T:
- deque
- hashmap
- hashset
- immut/array
- immut/hashmap
- immut/hashset
- immut/list
- immut/priority_queue
- immut/sorted_map
- immut/sorted_set
- queue
- priorityqueue
- rational
- sorted_map
- sorted_set
Build System Updates
-
Build Output Adjustment: The build process output has been adjusted to only print a command if that command fails.
-
Target Specification for
moon check|build|test|bundle: Previously, the--targetoption only supported three choices:wasm|wasm-gc|js. Now it supports specifying multiple backends to run in parallel. The supported options have changed towasm|wasm-gc|js|all, and they can be combined with commas. The--serialoption changes the parallel execution of different backends to serial execution, but the same backend will still execute concurrently. For example:moon test --target allruns tests for all backends.moon test --target js,wasmruns tests forjsandwasmbackends.moon test --target js,wasm --serialis equivalent to runningmoon test --target js; moon test --target wasmsequentially.
-
Memory Configuration in
moon.pkg.json: Addedheap-start-addressandimport-memoryconfiguration for["link"]["wasm"|"wasm-gc"]inmoon.pkg.json:
{
"link": {
"wasm": {
"heap-start-address": 65536,
"import-memory": {
"module": "xxx",
"name": "yyy"
}
}
}
}
- Default Protocol for
moon new: The default protocol formoon newhas been changed to Apache-2.0.